In a world of digital transformation, businesses are rethinking every stage of the customer journey and one of the most complex, yet critical, is the Order-to-Cash (O2C) process. From capturing a customer’s order to recognizing revenue in the books, this process involves multiple handoffs between departments, systems, and data models.
And in industries driven by subscription models, usage-based pricing, or bundled services, the billing stage becomes particularly challenging.
This is where SAP Convergent Invoicing (CI) proves invaluable.
SAP CI plays a central role in streamlining the O2C process, especially in the context of SAP’s Billing and Revenue Innovation Management (BRIM) suite. It ensures that usage data, fees, and pricing models are correctly transformed into customer-ready invoices and ultimately, into recognized revenue.
In this blog, we’ll explore how SAP CI fits into and elevates the entire order-to-cash cycle— from service usage to invoicing, payments, and revenue recognition.
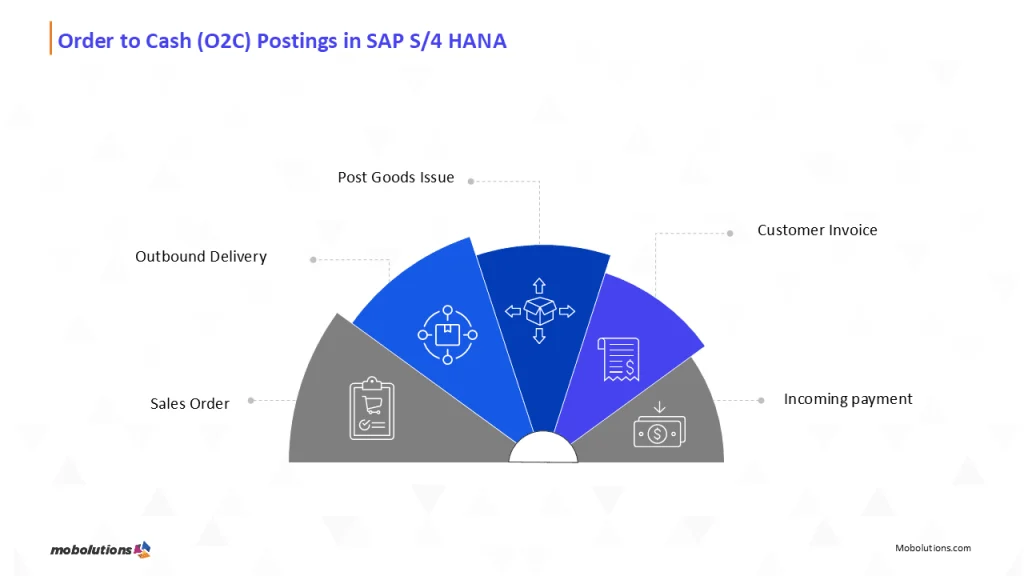
What is the Order-to-Cash Process?
The Order-to-Cash (O2C) process encompasses all the steps a company follows to fulfil a customer order and receive payment for it. While the concept sounds straightforward, the execution is anything but— especially in complex service-driven environments.
Typical Steps in an O2C Cycle:
- Order Capture
- Service Provisioning or Product Delivery
- Usage Collection (if applicable)
- Pricing/Rating (for usage or subscriptions)
- Billing/Invoicing
- Payment Processing
- Account Receivables and Collections
- Revenue Recognition
When dealing with high-volume, subscription-based, or pay-per-use business models like telcos, utilities, SaaS providers, and media platforms – the billing stage becomes the bottleneck. That’s where SAP CI takes center stage.
Where SAP CI Fits in the O2C Lifecycle:
Let’s look at how SAP CI maps into a modern O2C process:
SAP CI doesn’t replace other systems – it connects them, acting as the central orchestration layer for billing and invoicing in the O2C flow.
The Core Responsibilities of SAP CI in the O2C Process
1. Consolidating Billing Data from Multiple Sources
Most enterprises operate across diverse platforms. One customer might have:
- A subscription service
- Usage-based billing (e.g., data consumption, electricity usage)
- One-time purchases (e.g., hardware, activation fees)
SAP CI aggregates all these billable items from different source systems (CRM, Convergent Charging, ECC, or external platforms) and consolidates them into a single billing engine.
This consolidation improves invoice clarity and reduces disputes or delayed payments.
2. Supporting Flexible Billing Models
Today’s O2C cycles are not limited to one-size-fits-all models. Businesses may need:
- Monthly, quarterly, or milestone-based billing
- Tiered or volume-based pricing
- Prepaid and postpaid combinations
SAP CI is built to handle complex billing logic and adapt to diverse cycles.
For example:
A media streaming company may bill monthly for subscriptions, while also charging one-time pay-per-view events and usage-based advertising fees — all processed seamlessly through SAP CI.
3. Invoice Creation and Customer Communication
The invoicing step is more than a technical process – it’s a customer touchpoint.
SAP CI ensures:
- Clear, branded invoice layouts
- Line item explanations
- Language/currency localization
- Support for e-invoicing formats
For global enterprises, this level of clarity can dramatically reduce helpdesk queries and improve customer experience.
4. Revenue Assurance and Error Handling
Errors in billing can cause:
- Revenue leakage
- Customer dissatisfaction
- Compliance issues
SAP CI includes:
- Automated validations
- Manual and auto-correction tools (invoice reversals, re-billing)
- Audit trails for regulatory compliance
It also integrates tightly with SAP Revenue Accounting and Reporting (RAR) for accurate revenue recognition, especially important under standards like IFRS 15 or ASC 606.
5. Seamless Integration with Financial Systems
SAP CI connects directly with SAP FI-CA (Contract Accounts Receivable) for:
- Dunning
- Collections
- Payment processing
- Tax calculation
- Refunds and adjustments
The data from CI can then be posted into SAP S/4HANA General Ledger, ensuring that the financial backend mirrors the billing and customer activity accurately.
Real-World Example: SAP CI in a Telecom O2C Flow
Let’s look at a real-world telco example to bring this to life:
- Order: A customer signs up for a mobile plan.
- Usage: The system records data usage, calls, and roaming.
- Charging: SAP Convergent Charging calculates charges in real time.
- Billing: SAP CI collects all usage, monthly fees, and overages into a single invoice.
- Invoice Delivery: A PDF invoice is emailed and posted to the customer portal.
- Payment: The customer pays via auto-debit; payment is recorded in SAP FI-CA.
- Revenue Recognition: Subscription revenue is recognized monthly, usage revenue as consumed.
Without SAP CI, this complex blend of services, prices, and frequencies would be incredibly difficult to manage efficiently.
Key Advantages of SAP CI in the O2C Context
| Benefit | SAP CI Impact |
| Improved Cash Flow | Faster, accurate invoicing shortens time to payment |
| Reduced Disputes | Clear, consolidated invoices reduce customer confusion |
| Scalability | Supports millions of transactions and multiple business units |
| Flexibility | Enables innovation in pricing, packaging, and bundling |
| Compliance | Built-in audit trails and tax calculations |
| Globalization | Multi-currency, multilingual invoice support |
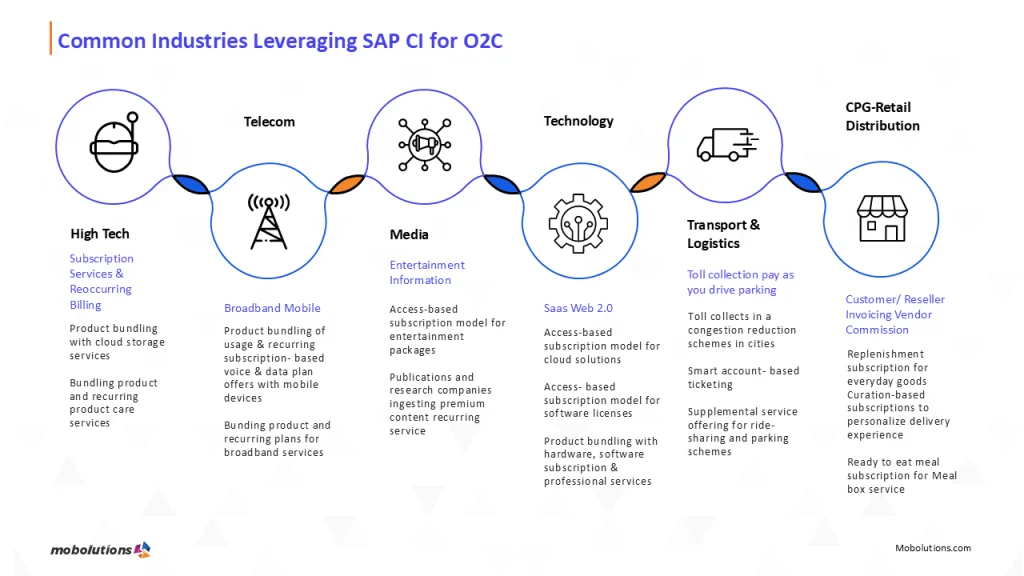
Common Industries Leveraging SAP CI for O2C
Telecom
Managing subscriptions, prepaid usage, roaming, data plans.
Utilities
Handling metered usage, government rates, and peak pricing.
SaaS/Cloud Providers
Blending recurring fees, usage-based compute/storage charges.
Media & Entertainment
Charging for streaming, ads, subscriptions, and live events.
Mobility/Transport
Pay-per-ride, dynamic pricing, monthly passes.
These industries have complex O2C cycles, making SAP CI a strategic necessity.
SAP CI vs Traditional Billing in the O2C Model
| Feature | Traditional Billing | SAP Convergent Invoicing |
| Data Sources | Limited, siloed | Multi-system integration |
| Invoice Consolidation | Manual or fragmented | Automated, unified invoices |
| Revenue Recognition | Decoupled from billing | Connected via SAP RAR |
| Adaptability to Pricing | Rigid | Real-time, dynamic models |
| Regulatory Compliance | Manual effort | Built-in with full traceability |
| Time to Cash | Delayed | Accelerated via automated cycles |
Futureproofing O2C with SAP CI
SAP CI is not just about solving today’s billing challenges – it’s about enabling future business models.
- As businesses move toward XaaS (Anything-as-a-Service), CI supports flexible combinations of product + service + usage.
- As real-time commerce grows (IoT, edge billing), SAP CI can process massive billing volumes with automation.
- As regulations evolve (digital tax, e-invoicing mandates), CI is continuously updated to remain compliant.
Wrapping Up
The Order-to-Cash process is no longer just a financial workflow— it’s a strategic pillar of customer experience, revenue realization, and business agility. In this landscape, SAP Convergent Invoicing (CI) is not a luxury – it’s a necessity.
From capturing usage, managing subscriptions, generating clear invoices, and enabling fast, accurate revenue recognition – SAP CI empowers businesses to scale smarter, bill faster, and get paid sooner.
If you’re looking to modernize your O2C process, SAP CI offers the stability, flexibility, and intelligence your business needs.
Ready to transform your O2C journey with SAP CI? Contact us today and see how we can help you get there faster.